Permissions and Roles: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The system has six user roles, each with different permission levels. Think of it as a video game tier list, but for business operations. 🎮 | The system has six user roles, each with different permission levels. Think of it as a video game tier list, but for business operations. 🎮 | ||
---- | ---- | ||
== Min Zinform 6 Version == | |||
The minimum system version for to enable roles is 6.1.13.0 | |||
== Role Hierarchy == | == Role Hierarchy == | ||
| Line 217: | Line 220: | ||
* '''Money = Admin Territory:''' Financial permissions deliberately restricted to admin roles. | * '''Money = Admin Territory:''' Financial permissions deliberately restricted to admin roles. | ||
* '''BaseUser:''' Currently has no explicit permissions. Define what they ''can'' do in your application logic. | * '''BaseUser:''' Currently has no explicit permissions. Define what they ''can'' do in your application logic. | ||
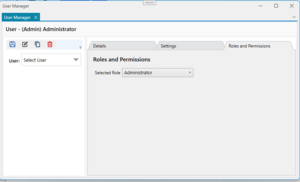
== Role Configuration == | |||
Roles are setup on the Users form from the Admin menu. | |||
[[File:Image RoleConfig.png|left|thumb]] | |||
Latest revision as of 01:36, 30 September 2025
User Roles & Permissions Guide
Overview
The system has six user roles, each with different permission levels. Think of it as a video game tier list, but for business operations. 🎮
Min Zinform 6 Version
The minimum system version for to enable roles is 6.1.13.0
Role Hierarchy
🦸♂️ Super Administrator
"God Mode Activated"
Full system access. Can do literally everything.
Key Permissions:
- All administrative functions
- Global settings configuration
- License management
- User management (create, update)
- Organization details
- Email & banking settings
- File & PDF imports
- Department management
- Document creation & updates
Use Case: System owner, IT director, or that one person who knows where all the bodies are buried.
👑 Administrator
"Almost Everything Except the Nuclear Codes"
Company-level admin with near-complete access. Currently identical to SuperAdmin (you might want to revisit this).
Key Permissions:
- Same as SuperAdministrator
- Access to all operational and administrative functions
Use Case: Senior management, operations director, trusted lieutenant.
⚠️ Note: The comments suggest CanAccessGlobalSettings and CanUpdateLicense should probably be SuperAdmin-only. Worth reviewing.
💪 Super User
"Power User with Training Wheels Off"
Can handle most day-to-day operations but can't mess with the company structure or users.
Key Permissions:
- ✅ Document management (create, update)
- ✅ File & PDF imports
- ✅ Department management
- ✅ Admin menu access
- ❌ Organization settings
- ❌ User management
- ❌ Financial settings
- ❌ License updates
Use Case: Team lead, operations manager, power user who gets stuff done.
⚡ Power User
"Operational Access, Hold the Danger"
More limited than SuperUser. Can manage departments but not much else.
Key Permissions:
- ✅ Department management
- ✅ Admin menu access
- ❌ Everything else
Use Case: Department head, mid-level manager, someone who needs organizational visibility but limited editing rights.
👤 Base User
"Standard Issue Employee"
Basic operational access. Can use the system but can't change anything structural.
Key Permissions:
- ❌ All administrative functions disabled
- Can view and use standard features (implied)
Use Case: Regular employees, data entry staff, most of your workforce.
👀 Read-only User
"Look But Don't Touch"
View-only access. The digital equivalent of a museum visitor.
Key Permissions:
- ❌ Everything is disabled
- ✅ IsReadOnly flag enabled
Use Case: Auditors, consultants, stakeholders, interns, or anyone who needs to see data but shouldn't change anything.
Quick Reference Matrix
| Permission | Super Admin | Admin | Super User | Power User | Base User | Read Only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organization Details | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Global Settings | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Admin Menu | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| License Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Document Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| User Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Email Settings | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Banking Settings | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| File/PDF Imports | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Department Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Read Only | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
Best Practices
- Start Restrictive: Assign the minimum role needed. You can always promote users later.
- Regular Audits: Review user roles quarterly. That intern from 2019 probably doesn't need SuperAdmin anymore.
- Separation of Duties: Keep financial and user management permissions limited to trusted admins.
- Document Changes: Log role changes, especially escalations to Admin/SuperAdmin.
Notes for Developers
- Admin vs SuperAdmin: Currently identical. Consider restricting
CanAccessGlobalSettingsandCanUpdateLicenseto SuperAdmin only. - Money = Admin Territory: Financial permissions deliberately restricted to admin roles.
- BaseUser: Currently has no explicit permissions. Define what they can do in your application logic.
Role Configuration
Roles are setup on the Users form from the Admin menu.